ANALYTICAL CENTER FOR DETERMINING THE QUALITY OF SOIL AND CROP PRODUCTION: OPPORTUNITIES AND PROSPECTS
Главная / News / Main news

In 2015, the “Scientific and Production Center of Grain Farming named after A.I. Barayev” LLP established an Analytical Center for determining the quality of soil and crop products, which is accredited according to GOST ISO/IEC 17025-2019 “General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories”, also constantly extends its accreditation and expands its scope.
The Analytical Center includes three laboratories: the laboratory of biochemistry and technological assessment of the quality of agricultural crops, the laboratory of soil and agrochemical research and the laboratory of microbiology, which perform tests to determine the indicators of crop production and soil quality.
Analytical work is carried out by specialists who have been trained and have work experience within their competence. The research staff of the Analytical Center constantly improve their qualifications, participate in scientific conferences, study in graduate school, have academic degrees and scientific publications.
The Analytical Center constantly updates the instrumentation of analytical laboratories. The Laboratory of Soil and Agrochemical research has equipment for the determination of total nitrogen UDC-139 (Sweden), for the determination of trace elements atomic absorption spectrometer AA-140 (Austria), for the determination of pH multichannel analyzer of anions and cations in liquid media PIAC (Russia). In 2018-2021 a flow analyzer from San++ (Netherlands) was purchased, which allows automating standard analyses, increasing laboratory productivity, and a PrimacsCN100 carbon and nitrogen analyzer (Scalar). Due to the upgrade of analytical equipment, the productivity, quality and accuracy of research increases.
The presence of high-precision equipment and first-class specialists in the accredited center allows conducting agrochemical and microbiological studies of the soil, and biochemical and technological evaluation of crop production.
Soil and agrochemical research
Farmers who want to get high yields need to know that an important condition for getting a good harvest is conscious work on creating soil fertility. Agrochemical analysis helps to comprehensively investigate the properties of the soil. What elements should be identified in the soil first? These are mobile or nutritious macronutrients: nitrate nitrogen, mobile phosphorus and potassium, mobile sulfur, organic matter and pH of the soil solution, which play a major role in the growth and development of plants.
Humus is important in the formation of soil fertility. With a lack of nitrogen, humus decomposes, which leads to an increase in nitrogen in the soil. If a farmer does not apply mineral fertilizers, then for several years he can get a crop by using humus, but this is a temporary measure. If nitrogen-phosphorus fertilizers are not applied for several years, this will lead to a gradual decrease in soil humus and deterioration of agrophysical and agrochemical properties of arable land. Therefore, farmers should not bring the situation to a critical moment. To do this, it is recommended to conduct an agrochemical examination of the soil, which will allow you to determine the content of nutrients.
Agrochemical examination is carried out in several stages. The first stage is the departure of a group of specialists on the selection of soil samples to farms. The selection is carried out according to the method by which the field is divided into several plots, possibly of different areas from 1 to 75 hectares. Soil samples are taken by following a given cell in a zigzag pattern. Soil samples are mixed and one sample is obtained for each site. As a result, the number of samples equal to the number of sites is obtained. Then the soil samples are dried and ground for further agrochemical analysis.
At the next stage, a comprehensive agrochemical survey is carried out on indicators characterizing soil fertility and included in the scope of accreditation: analyses to determine soil nutrients: nitrogen (total nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen), mobile phosphorus, exchangeable potassium, organic matter, pH of aqueous extract and mobile sulfur. At the request of clients, the list of investigated indicators can be expanded.
The laboratory can perform analyses to determine: dense soil residue, ions Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, CO32-, HCO32-, Cl-, SO42- in water extract, pH salt extract, trace elements (Cu, Co, Cd, Zn)
The last stage of the agrochemical field survey is the processing of the results of the data obtained and their delivery to the customer, which include:
1. Protocol of results;
2. Report on agrochemical research on the farm;
3. Recommendations for fertilization;
4. Cartograms on the content of soil nutrients of mobile forms of phosphorus and exchangeable potassium, organic matter, nitrogen and mobile sulfur.
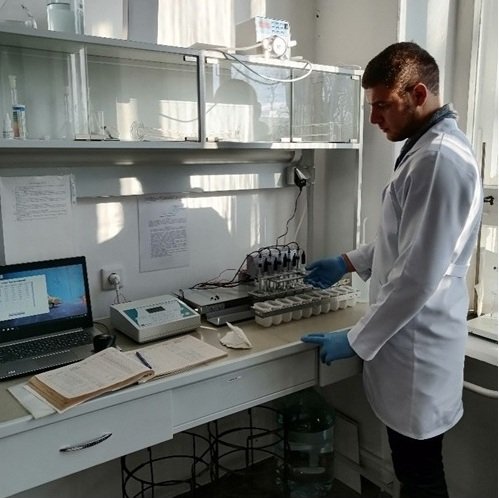

Determination of pH on a multichannel analyzer PIAK-5
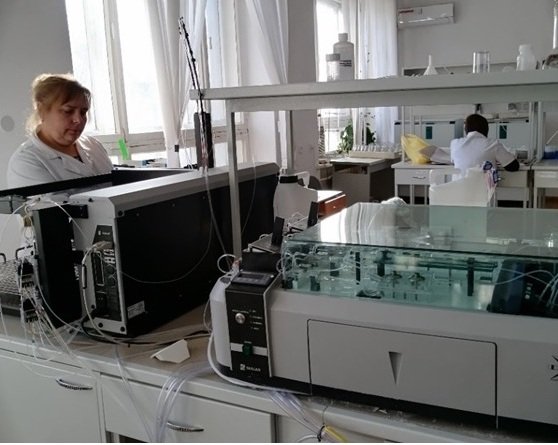

Determination of mobile phosphorus and exchangeable potassium on the San++ analyzer
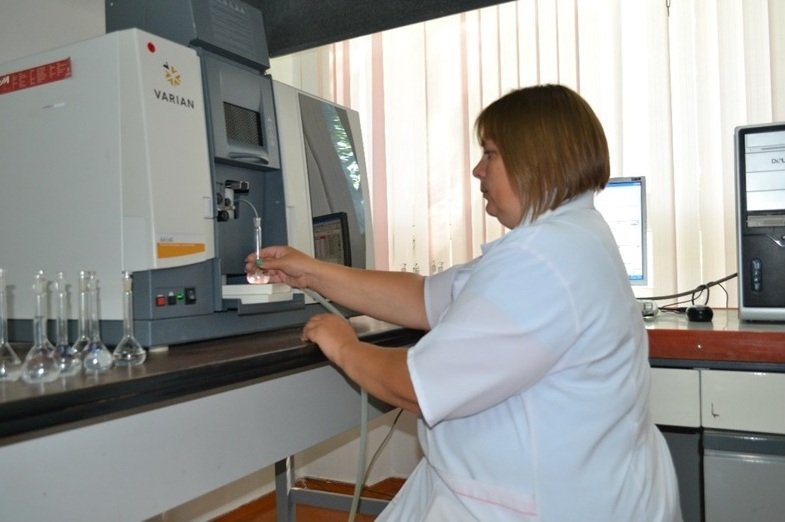

Determination of trace elements in soil on an atomic absorption spectrophotometer
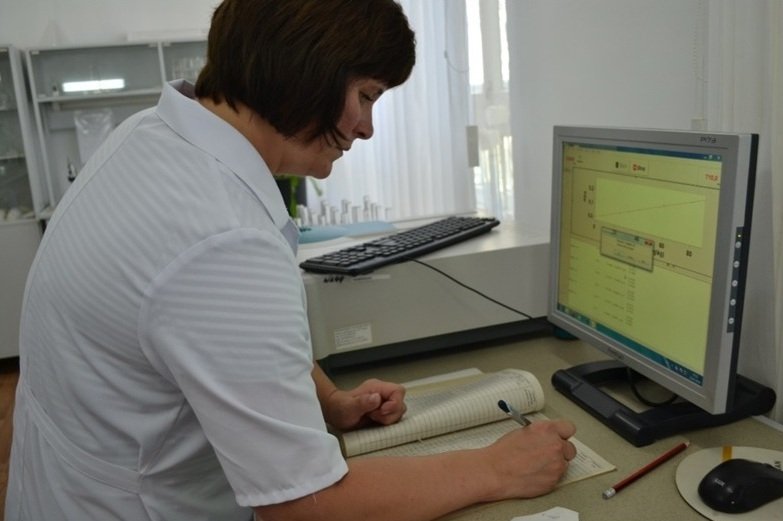

Determination of the concentration of nutrients in the soil on a spectrophotometer
Microbiological studies
The study of soil is not only the determination of macro and microelements, but also the identification of the relationship between living organisms. Microorganisms play a leading role in the nitrogen cycle, which limits the productivity of most terrestrial ecosystems and are sensitive bioindicators. Soil microflora and microbiological processes also play an important role in soil fertility. The productivity of agricultural land is determined by the composition and spectrum of soil microbiocenosis, since the processes of microbiological transformation of matter occurring in it affect the conditions of plant growth and nutrition.
In this regard, it is very important to determine the soil microbiocenosis under crops. Such studies are conducted in the microbiology laboratory. Laboratory staff carry out the selection of soil samples in the field under crops of agricultural crops along the horizons of the soil profile, in laboratory conditions carry out soil sample preparation and microbiological sowing. This analysis makes it possible to determine the numerical composition and identify ecological and trophic groups of microorganisms, as well as the presence of phytopathogens that cause plant diseases and soil toxicosis. In addition, these indicators allow us to establish the direction of microbiological processes occurring directly in the soil under agricultural crops.
In addition to studies of soil microbiocenosis, phytopathological analysis of seed material and grain for infection with microorganisms, including phytopathogenic ones, is also carried out. The analysis is conducted for latent infection by pathogens of phytopathogenic fungi and general contamination by epiphytic microorganisms. Why is it important to conduct such research? The fact is that seeds are one of the main sources of the spread of diseases. The infectious origin may be on the surface of the outer shell of healthy seeds. This infection does not directly affect them and only penetrates into seedlings when seeds germinate. Spreading in an adult plant, this infection contributes to the outbreak of the disease in crops. In addition to parasitic microorganisms, which include the smut of cereals, saprophytic microorganisms – bacteria and fungi - grow and develop on seeds under certain conditions. Most often this happens when the humidity of the seeds is increased due to the wet weather that stood during the ripening or harvesting period, as well as during the storage of seeds at high humidity.In this case, the increased development of saprophytic fungi or bacteria is accompanied by mold or rotting of seeds. The presence of even a small number of infections in seeds can be a favorable factor for the development of an outbreak of diseases. Therefore, in order to prevent the development of plant diseases in the field, it is necessary to examine seeds as one of the primary sources of many diseases. Phytopathological analysis of seeds, allows you to make a timely decision about the need for their treatment, to choose a preparation and dosage for the treatment of seed material, as well as to predict the development of diseases during the growing season.
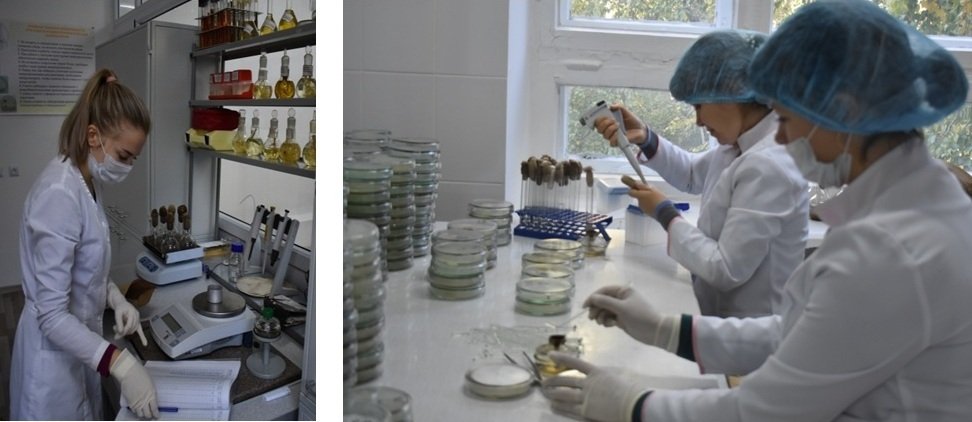

Preparation of soil canopies Microbiological sowing of soil samples
for microbiological analysis
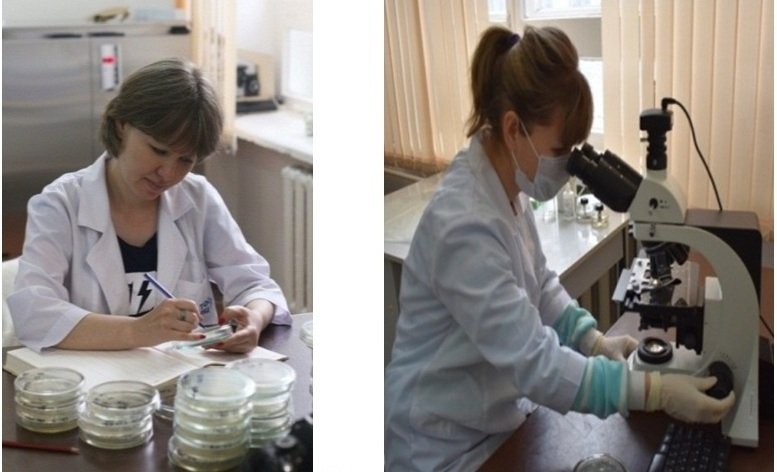

Accounting of soil microorganisms, Microscopy of soil microorganisms grown on nutrient media
Biochemical and technological research
One of the resulting indicators of the success of any agricultural technology is its yield and the quality of the resulting grain. These studies are carried out by the laboratory of biochemistry and technological assessment of the quality of agricultural crops. Our specialists conduct research on quality control of agricultural products in the process of creating new varieties and technologies.
The work uses chemical and express methods for determining quality indicators using infrared analyzers, quality assessment on instruments and equipment, interstate, national and international standards.
Evaluation of grain quality indicators of soft wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), durum wheat (Triticum durum). It is carried out starting from early breeding nurseries, when there is still very little grain, the indicators of SDS sedimentation and protein content in the grain are determined. In senior breeding nurseries, in addition to these indicators, studies are added on devices, determination of gluten content, physical properties of the test on an alveograph and a pharynograph, evaluation of the baking properties of soft wheat and the pasta virtues of durum wheat. In addition, the determination of the color characteristics of durum wheat grain and semolina in the Lab system, according to the colorimeter CR-410 of KonicaMinolta (Japan).
The scope of accreditation includes the determination of odor, color, weed and grain impurities, typical composition, humidity, nature, quantity and quality of gluten according to the national standard of the Republic of Kazakhstan and international ISO, gluten index, protein content, number of drops, vitreousness, mass of 1000 kernels, content of carotenoid pigments, alveographic and pharynographic studies of rheological properties test, laboratory baking of test loaves.
In grain fodder (barley, oats) legumes (peas, chickpeas, lentils), oilseeds (sunflower, rapeseed, flax) crops in grain and oilseeds, it is possible to determine the smell, color, humidity, protein content, weight of 1000 kernels. For oilseeds, additional indicators will be clogging, oil content, fatty acid composition of oils (saturated and unsaturated acids), the content of glucosinolates, erucic acid in rapeseed.
Fodder crops are evaluated according to the results of zootechnical analysis: chemical composition and nutritional value - moisture content, crude protein, crude and detergent fiber, crude fat, crude ash, carotene. The exchange energy and feed units are calculated according to quality indicators.
The Analytical Center plans to determine the quality of soil and crop production with the task of equipping with advanced devices and equipment, as well as working out new methods of analysis in the field of plant biochemistry, soil analysis and microbiology.
For a more detailed study of the quality of grain and wheat flour, a Mixolab from Chopin, France, will be purchased, which is designed to control the dynamics of the rheological behavior of the dough during kneading by the nature of the change in the torque value on the drive of the kneading tank and determine the following indicators: the water absorption capacity of flour (WAA), the time of dough formation, its stability and the value of liquefaction, as well as the consistency of the dough during heating.
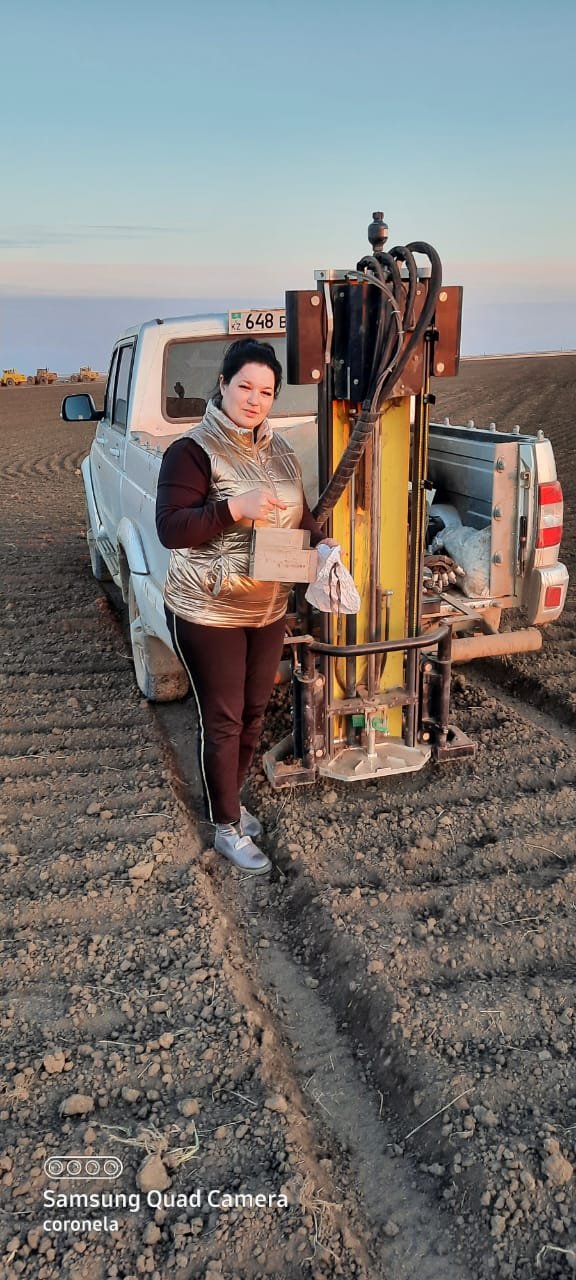
It is planned to study various types of soil carbon (total, organic and inorganic carbon) on the PrimacsCN100 nitrogen and carbon analyzer. To identify the enrichment of humus with nitrogen. Determine the microbial biomass of the soil. A group of soil sampling is being created on the basis of the Analytical Center. Its task is automated selection of soil samples in the fields of farms with strict observance of selection methods. Currently, it is equipped with one soil sampler Wintex 3000 (Denmark) based on UAZ PICKUP, it is planned to purchase a second automatic sampler to increase productivity.
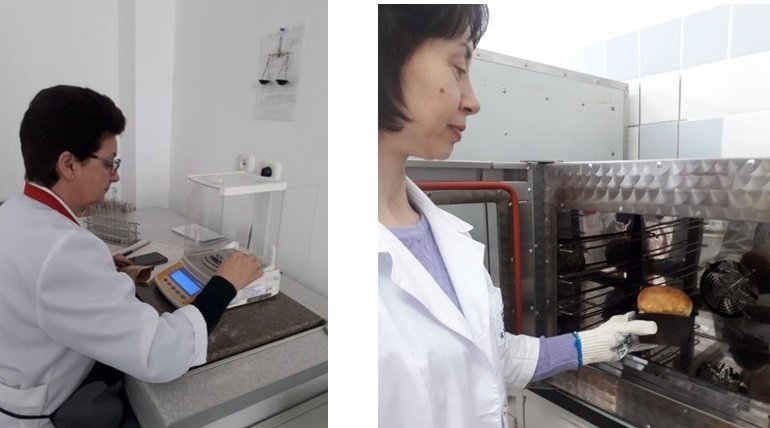
Taking a sample of plant samples Trial laboratory baking of bread

| Determination of amino acid composition of grain crops | Determination of rheological properties of spring soft wheat dough |

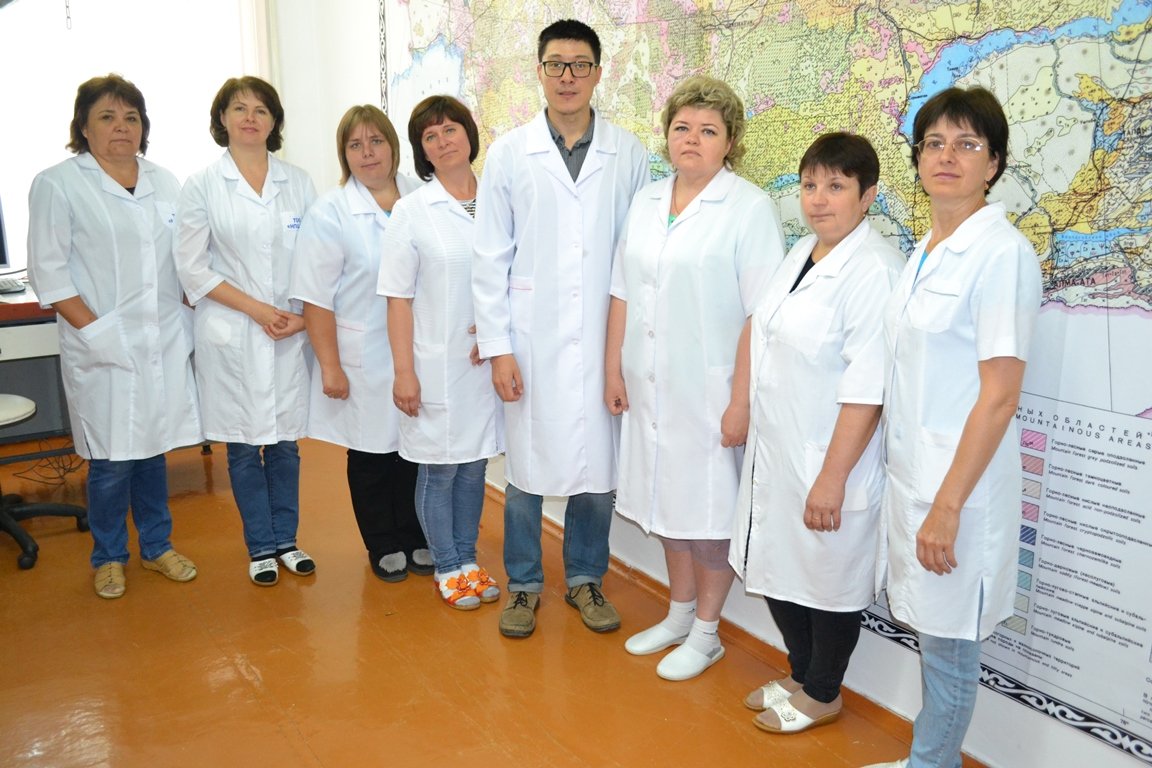
The staff of the Analytical Center for Soil quality and crop production
If you need to conduct comprehensive research on agrochemical analysis of the soil, determine its microbiocenosis, as well as assess the quality of agricultural products, you can contact the following contact details:
“Scientific and Production Center of Grain Farming named after A.I. Barayev” LLP,
Phone number: +7 (71631) 2 – 30 – 29, E-mail: tsenter-zerna@mail.ru
































